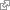extra-ocular muscle
Skeletal muscle derived from cranial mesoderm and controls eye movements. [ http://amigo.geneontology.org/amigo/term/GO:0002074 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extraocular_muscles ]
Synonyms: extrinsic ocular muscle, extraocular skeletal muscle, extrinsic muscle of eyeball, extrinsic eye muscle, extra-ocular skeletal muscle, extraocular musculature, extraocular muscle
Term info
- TAO:0000511
- SCTID:181150000
- AAO:0010028
- BTO:0001579
- CALOHA:TS-0305
- EHDAA:5729
- FMA:49033
- EMAPA:18234
- VHOG:0000549
- EHDAA2:0000482
- Wikipedia:Extraocular_muscles
- EFO:0001921
- MA:0001271
- ZFA:0000511
uberon_slim, efo_slim, pheno_slim, vertebrate_core
Any of the six small muscles that control movement of the eyeball within the socket. [TFD][VHOG], Muscles surrounding the eye (bulbus oculi) and having an effect on eye movements.[AAO]
The ability to rotate the eyeball is common to all vertebrates with well-developed eyes, regardless of the habitat in which they live, so these (extrinsic ocular) muscles tend to be conservative. They change little during the course of evolution.[well established][VHOG]
extraocular
Mammals have 7 extra-ocular muscles, but humans lack the M. retractor bulbi.
Myofibers in extraocular muscles are derived from mesoderm, whereas muscle connective tissue cells arise from neural crest.[PMID:16638982]
BTO and MA consider this part of the eye; we follow them here (inferred from skeletal muscle). Not clear if omission from FMA is deliberate.
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/61/MRI_of_human_eye.jpg
todo - resolve discrepancies in which muscles are considered extra-ocular
musculi externi bulbi oculi
UBERON:0006229
uberon
UBERON:0001601
Extra-ocular muscle